Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized the cybersecurity landscape, making it better at detecting and handling threats but it also brings new risks and challenges. Organizations need to know and understand the dark side of AI in cybersecurity as well to strategize their defense mechanisms more effectively. By balancing the pros and cons, businesses can use AI to boost productivity.
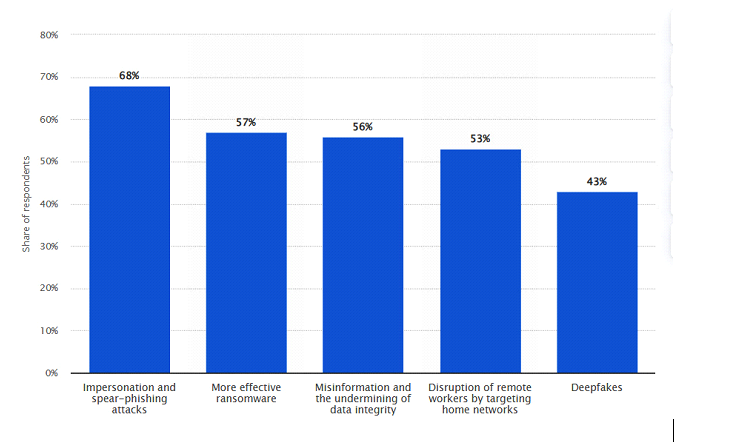
According to a report submitted by Statista, they stated, “In 2021, around 68 percent of survey respondents stated that Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used for impersonation and spear-phishing attacks against their companies in the future. AI can also be used to enhance ransomware, which could become a real danger to companies’ IT security.”
Risks associated with AI in cybersecurity.
Malware
AI can be used to develop polymorphic malware. This type of malware possesses the ability to alter its code dynamically, making it exceedingly difficult for traditional antivirus programs to detect and neutralize it. By leveraging AI, attackers can create malware that continually evolves, enhancing its ability to evade detection and maintain persistence within targeted systems. This use of AI in cybersecurity presents challenges for professionals and underscores the dual-edged nature of AI.
Phishing
AI can create personalized phishing emails by analyzing social media profiles and other data. These targeted emails are much harder to recognize as fraudulent, significantly increasing the attacker’s success rate. As a result, individuals are more likely to fall for these scams, posing a substantial risk to businesses. This capability of AI in cybersecurity makes phishing attempts more effective and dangerous for both individuals and organizations.
Automated attacks
AI can launch automated attacks in cybersecurity with great efficiency. These attacks can operate on their own, targeting systems and disrupting services without requiring human intervention. The speed and scalability of AI-driven attacks make them very dangerous. They can quickly overwhelm networks and cause significant damage, posing a serious threat to network stability and security, highlighting the need for stronger defences against such threats.
AI model inversion
Attackers can use data poisoning to introduce harmful data into AI training sets, messing up the AI’s learning, which leads to wrong or harmful decisions. Misusing AI data can also cause biased or unethical results. Both issues weaken the reliability and effectiveness of AI systems in cybersecurity, making them less trustworthy and more prone to errors. This kind of vulnerability also leads to data privacy and compliance violations.
Surveillance
AI-driven security systems can improve surveillance, but they might invade privacy. These systems can monitor and analyze huge amounts of data quickly, raising concerns about balancing security with privacy. If used with harmful intentions, AI surveillance can also impact businesses by damaging their reputation and trust. Organizations need to handle these issues carefully and follow privacy laws to protect individual rights and maintain trust.
Complexity of AI systems
AI systems can be complex and prone to failures or misconfigurations. These issues can lead to significant security breaches if not properly addressed. Keeping AI systems reliable requires regular monitoring and maintenance to prevent malfunctions that could compromise an organization’s cybersecurity. It’s crucial to stay vigilant and fix any problems promptly to ensure the security of the system and protect against potential threats.
No comments:
Post a Comment